WHAT IS ELECTRICITY?
1) Electricity is an Energy.
2) Energy which does the work
Facts about Electricity:
(i) It travels at the speed of 297841 Km/sec.
(ii) In India, voltage generation is A.C and is at 11KV.
(iii) The generation is at 50 Hz.
(iv) Shock - AC Voltage - 325 V DC Voltage - Same V
(v) All equipments are connected in parallel.
(vi) It cannot be seen, only the effects of electricity can be seen/felt.
(vii) Current always takes shortest route to complete the circuit.
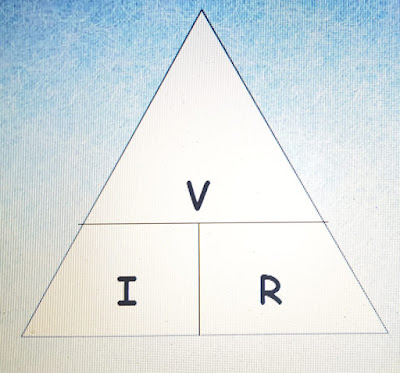
Magic Triangle of Electricity:
SOME IMPORTANT TERMS/DEFINITIONS:
• Voltage: It is the potential difference between two points.
• Current: It is flow of Electrons.
• Frequency: No. of Cycles/Second.
• Resistance: This apposes flow of current.
• Conductor: This offers least resistance to flow of current.
• Insulators: This offers maximum resistance to flow of current.
WHAT IS CURRENT??
• Flow of electrons in any conductor is called Current. The unit of current is Ampere.
• It is not possible to see the flow of electrons or current but electric current can be felt by its effects.
There are five effects :
1. Physical Effect.
2. X-ray Effect.
3. Heating Effect.
4. Chemical Effect.
5. Magnetic Effect.
Physical Effect
• Our body is a good conductor. Current can easily pass through it. When body touches the bare conductor carrying conductor, current flows from the body to earth and the body gets a shock. The
effect of electric shock may result in death.
X-Ray Effect
• When a very high frequency voltage is passed through vacuum tube, a special type of rays emerge which cannot be seen. These rays are called X rays. X rays are used in Hospitals etc.
Heating Effect
• When current is passed through a conductor, heat is produced in that conductor and such effect is used in heaters, iron, electric lamps and soldering iron etc.
Chemical Effect
• When current is passed through the electrolyte (acid mixed water), chemical action takes place. Such effect is used in battery charging, electroplating etc.
Magnetic Effect
• When conductor is wound around an iron piece and an electric current is passed,magnetic field is produced around the conductor. This effect of electricity is used in Fans, electric bells, meters etc.
Types of Voltage & Current
• There are two types of Voltage & Electric Current
1) A.C. Voltage & A.C. Current (Alternating Current)
2) D.C. Voltage & D.C. Current (Direct Current)
Advantages of A.C. Over D.C.
A.C. means alternating current The current which alternates its direction and magnitude every time.
95% of the total energy is produced, transmitted and distributed in A.C.Supply.
Following are some of the reasons :
1. More voltage can be generated than D.C.(up to 33,000V) whereas in D.C. Upto 650V only.
2. A.C. Voltage can be varied i.e. Increased or decreased with the help of transformer.
3. A.C. Transmission and distribution is more economical as line material can be saved by transmitting power at a higher voltage.
4. A.C. Motors of the same horsepower as of D.C. Motors are cheaper, require lesser space and less maintenance.
5. A.C. Power can be easily converted to D.C. Supply whereas D.C. Supply cannot be converted to A.C. easily and is also not economical.
Advantages of D.C. Over A.C.
D.C. Means direct current The current which does not change its direction and magnitude. Even though
we produce 95% power in A.C. But we cannot forget the merits of D.C. Power.
1. D.C. Motors are most suitable for railways, cranes and lifts.
2. D.C. Is required for electroplating, battery charging etc.
3. Arc lamps for searchlights and cinema projectors work on D.C.
4. Arc welding is better in D.C. than A.C.
5. Where fine speed control in both directions is required as in rolling mills, paper mills, D.C. Motors are required.
RANGE OF VOLTAGES
• Where voltage does not exceed 250V (0-250V) - Low Tension (L.T.)
• Where voltage does not exceed 650V - Medium Tension (M.T.)
• Where voltage does not exceed 33,000V - High Tension (H.T.)
• Above 33,000V -Extra High Tension (E.H.T.)
Comments
Post a Comment