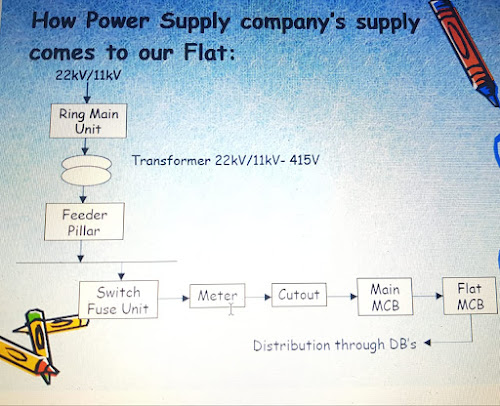
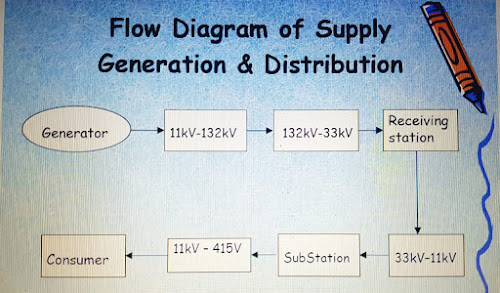
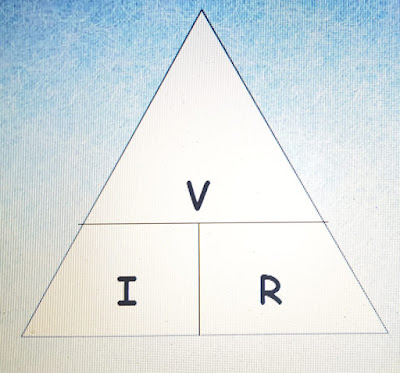
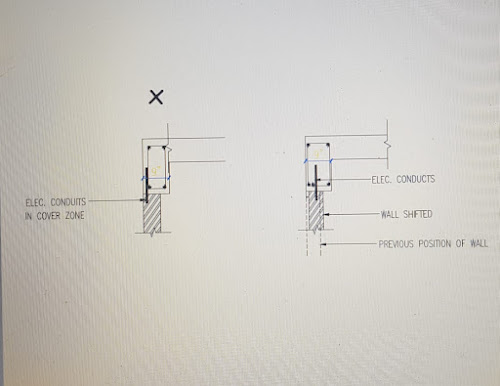
What is the purpose of keeping tremie pipe’s tip immersed in freshly-placed concrete for about 1m in underwater concreting?
What is the purpose of keeping tremie pipe’s tip immersed in freshly-placed concrete for about 1m in underwater concreting? The size of tremie pipe is about 300mm with sections having flange couplings fitted with gasket to prevent water leakage. The tremie pipe should be closed initially to prevent water from entering the pipe. It should be designed with sufficient thickness and weight so that it would not be buoyant when empty inside water. The placement of tremie concrete is commenced by putting the closed pipe underwater to the location for concreting, followed by partial filling of tremie pipe with concrete. In order to have tremie concrete flowed out of the pipe, it is necessary to fill the pipe with concrete of sufficient height to overcome the water pressure and frictional head. After that the tremie pipe is raised about 150mm to allow concrete to flow out. To enhance sufficient bonding, each succeeding layer of concrete should be placed before the preceding layer has reached